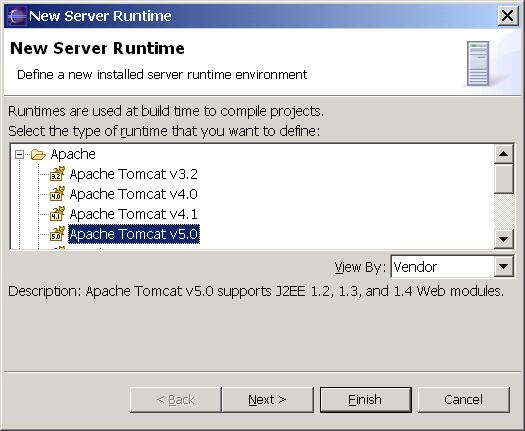
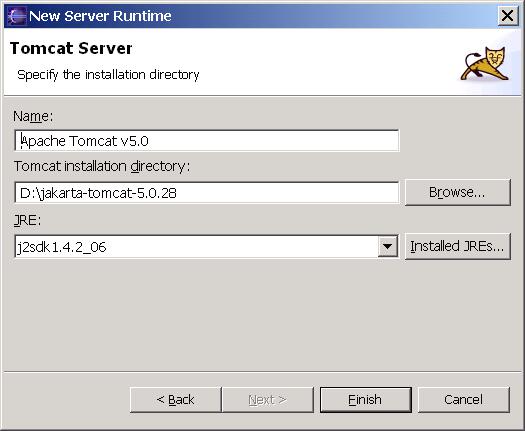
You have 2 options:
1. Edit eclipse-home/eclipse.ini to be something like the following and restart Eclipse.
1. Edit eclipse-home/eclipse.ini to be something like the following and restart Eclipse.
-vmargs
-Xms64m
-Xmx256meclipse -vmargs -Xms64m -Xmx256m